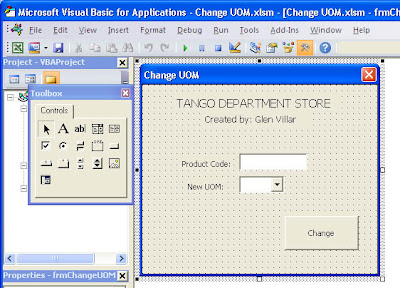
Figure 1.
There
are times when your boss calls for an immediate solution for a simple
problem but that can only be solved by your programming skill.
You
look at the problem, analyze a solution within the scope of the
software the company is currently using and work it out from there.
But
what if the problem is just a glitz in a working system? For instance, a
messed up department code or an error in unit of measurement? Of
course, as much as possible we go by what the POS can do about it. But
what if the POS doesn't provide solution to that problem?
This
is where you intervene as an I.T. Manager or a Database Administrator.
Suppose you can revert the error in the SQL Server by executing
queries? That'll solve the problem provided that you know the in and out
of your POS system.
In the real
world however, such a mistake can be recurring and sometimes inevitable
and you may not be there to always solve the problem. So the ultimate
solution is to create an app that shall call a stored procedure that
contains a script which corrects the error so that anyone in the
company can resolve the problem, be it the supervisor or the store
owner.
But
trust me, the boss won't always bother about working with an app made in
VB or Foxpro or .net, let alone the time your boss was forced to move
out of his/her table because you needed to install a few runtime dll's
for the app or the app itself. But luckily, most of the bosses have
something in common, they all love to work with MS Excel.
So,
more likely, the most elegant solution is excel programming. Yes,
that's right, macro programming. It's simple, and straightforward. Your
boss is gonna like its simplicity.
In
this tutorial, I'm going to demonstrate how we can create a form in MS
Excel, drop some controls on it and populate a control. This shall
include a way to execute a stored procedure saved in SQL Server within
the excel environment.
Creating the Form
1. Open MS Excel.
2. Open a New Workbook.
3. Now, we need to use the Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications by pressing Alt+F11. See the fig. below.
4.
At the left side, under the VBA Project window, right click on the
ThisWorkbook, select Insert and choose UserForm. You should get a blank
form named "UserForm1" after that.
 5.
I'm gonna fast forward a bit and skip some parts to go ahead with the
important part of this tutorial. Please refer to the images named Figure
1 which is at the beginning of this article. That should be the final
outcome of this article. Try to copy that form by dropping a textbox, a
command button and a few label onto the form.
5.
I'm gonna fast forward a bit and skip some parts to go ahead with the
important part of this tutorial. Please refer to the images named Figure
1 which is at the beginning of this article. That should be the final
outcome of this article. Try to copy that form by dropping a textbox, a
command button and a few label onto the form.
Notice that there's also a combo box on that form. I used a combo box for items which are repetitious like in this example:
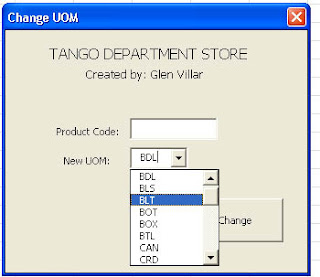 Adding the Code
Adding the CodeSo to populate the combobox, just double click the form named UserForm1 and place this code in the Initialize event.
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
With Me.ComboBox1
.AddItem ("BAG")
.AddItem ("BDL")
.AddItem ("BLS")
.AddItem ("BLT")
.AddItem ("BOT")
.AddItem ("BOX")
.AddItem ("BTL")
.AddItem ("CAN")
.AddItem ("CRD")
.AddItem ("CTN")
.AddItem ("DOZ")
.AddItem ("EA")
End With
Me.ComboBox1.ListIndex = 1
End Sub
Populating
a combobox is easy using the .AddItem method. I provided the .ListIndex
= 1 so that it automatically shows the first item when the form is
shown.
In this tutorial, we are
just going to use 3 events. One is the form's Initialize and the second
is the command button's click event which should execute a stored
procedure in SQL Server. The third one is the button in the main sheet
which should call out the form that we've just created.
Double
click on the command button that you've just added on the UserForm1.
Select the Click event and add the following codes below.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
If Me.TextBox1.Text = "" Then
MsgBox ("Please enter the product code.")
Me.TextBox1.SetFocus
Else
Dim lcPC As String
Dim lcUOM As String
lcPC = Trim(Me.TextBox1.Text)
lcUOM = Trim(Me.ComboBox1.Value)
Dim lcCMD As ADODB.Command
Dim lcCon As ADODB.Connection
Set lcCMD = New ADODB.Command
Set lcCon = New ADODB.Connection
lcCon.Open ("DSN=MYDATABASE;UID=me;pwd=password")
With lcCMD
.ActiveConnection = lcCon
.CommandText = "execute gtv_sp_ChangeUOM " & "'"
& lcPC & "'" & "," & "'" & lcUOM
& "'"
.Execute
End With
MsgBox ("Item has been changed successfully!")
End If
End Sub
I
used ADODB to handle the connection and execution of stored procedure. I
also referred to a DSN named MYDATABASE that I've just set up. Setting
up a DSN name is easy and I'll show you next time how to do that. This
code will work provided that the DSN name, username and password is
correct and the stored procedure being called exists in the SQL Server.
Basically,
the whole point of that code is to execute a parameterized stored
procedure. The two parameters will come from the textbox' value and from
the combo box value. Notice that I assigned their values in two
variables and later concatenated the necessary command and parameters in
a single string.
To call that
form in the excel sheet, we need to drop a command button on Sheet1
itself. So switch back to the excel sheet and click the Developer tab
on the Menu bar. Click Insert and select the command button. It should
bring you to this:
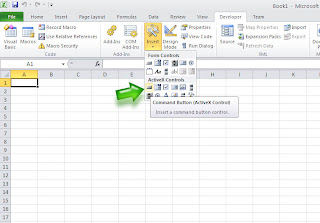 Now,
click on any cell in sheet1. A button will be attached on the sheet.
Right click on that button and select Assign Macro and place the code
below:
Now,
click on any cell in sheet1. A button will be attached on the sheet.
Right click on that button and select Assign Macro and place the code
below:
Sub Button1_Click()
UserForm1.Show
End Sub
When
this button is clicked, the form will be shown and you can readily use
that to execute the stored procedure being called. Make sure that you
save the file in Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook (*.xslm) format.
That's it. You can distribute this file to your boss and she/he can use it in no time with ease.

No comments:
Post a Comment